BiOmega
Take a Deep Dive on the Body and Brain Benefits of USANA® BiOmega™
USANA® BiOmega™
Concentrated omega-3 fats from fish oil plus vitamin D support your heart, brain, eyes and more, starting at the source of health—your cells.
Get the beneficial fats your body and brain need to be at their best with USANA® BiOmega™. No healthy nutritional program is complete without a high-quality source of omega-3s. These fatty acids work to keep you healthy from before birth through your senior years. And your body can’t make many omega-3s on its own. So, eating fatty fish a couple times a week is one way to boost your intake. But adding USANA BiOmega every day makes it easy to get plenty of omega-3s in your diet.*
BiOmega is made with a concentrated dose of premium quality, purified fish oil to deliver a multitude of benefits for your daily wellness. Thousands of studies have shown omega-3s help support several aspects of health:*
- Cellular function
- Balanced immune response
- Cardiovascular health
- Brain and nerve activity
- Eye health
- Healthy pregnancies
- Joint and exercise recovery
Plus, research continues to reveal benefits for omega-3 supplementation, including liver and breast health. And that’s not all. This multitasking supplement is fortified with vitamin D for even more support for your cells—where great health starts.*
Beyond the added vitamin D, the key to BiOmega’s effectiveness is the amount of long-chain EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) it contains. Both EPA and DHA have been extensively studied and found to provide different, important actions in the body. And the long-chain forms of omega-3s are more potent than other, short-chain fatty acids. This means you don’t have to consume as much to get all the great health benefits.*
What are long- and short-chain fatty acids?
Fatty acids are the main component of lipids (fats) in your body. They are made up of carbon atom chains (with some other molecules, too). The carbon chains have different lengths. They’re referred to as long, medium, or short based on the number of carbons they have. Fatty acids are considered short-chain if they have one to six carbons, medium if they have seven to 12, and long-chain with more than 12.
These individual fatty acids serve different purposes in the body based on their chain length. Alpha-linoleic acid is a short-chain fatty acid that can be converted to long-chain fatty acids, like DHA, in the body. However, the process isn’t as efficient as eating DHA or EPA directly. It’s still healthy. You just need to consume more ALA to get the same benefit. This is why getting it already formed in a long chain through the diet is helpful for meeting your body’s nutritional demands.*
BiOmega offers one of the most concentrated doses of EPA and DHA you can find. It’s made from responsibly sourced, cold-water, deep-sea fish. Plus, it’s flavored with lemon oil to help minimize any fishy aftertaste. (Taking your supplement with a meal should also help reduce any aftertaste issues.) All of this adds up to making BiOmega a great catch for supporting your whole-body health.*
Get the Facts About Fats
Fats are an essential part of your diet. However, you should limit unhealthy fat intake and focus on consuming the right kinds of fats.
The fats you should limit are saturated and trans-fats. Saturated fats are found in red meat, milk, butter, and cheese. They are not as harmful as trans fats but should be eaten in moderation. Trans-fatty acids (found in partially hydrogenated vegetable oils) are even more harmful to your health. Try to avoid them, or at least limit them, in your diet. These are fats that are solid at room temperature. They promote an increase in low-density lipoproteins (LDL–the bad cholesterol) and the formation of artery-clogging fatty deposits.
The good guys are monounsaturated fats found in vegetable oils, avocados, nuts, and seeds. That’s because they don’t promote arterial fat deposits. And polyunsaturated fatty acids—especially omega-6 and omega-3—are the most beneficial to overall health.*
Omega-6 fatty acids are found in poultry, leafy greens, eggs, nuts, grains, and vegetable oils.
There are many types of omega-3s, but the three you hear about most are alpha-linoleic acid, EPA, and DHA. Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are plant-based sources of alpha-linoleic acid, which converts to EPA and DHA in the body. You can get EPA and DHA omega-3s directly from food sources, like fatty fish—salmon mackerel, tuna, sardines, and anchovies—or krill oil.
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids compete for the same enzymes that trigger production of eicosanoids in your body (more on this below). And, it’s important that you have a good balance of each to make sure you get the benefits of both.*

Many experts believe a 1:1 ratio of omega-3 and omega-6 is ideal. But a 4:1 ratio is a good target for most people for overall health. However, average diets often contain significantly more omega-6 fatty acids, because they’re found in many processed foods. It’s not uncommon to see ratios of 16:1 (or higher) of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids.*
This means omega-6s could be blocking the benefits of the omega-3s in your diet. And omega-3s may not be present to counteract an excess of omega-6s, which could have a negative impact on your health.*
Unfortunately, this imbalance is common. Despite the clear health benefits associated with omega-3 fatty acids, dietary surveys indicate up to 90 percent of people simply don’t get enough from their diet. Most individuals only consume 30-100 mg of EPA/DHA daily, falling far below the recommended amounts of between 250 mg to 2 grams of EPA/DHA per day.
Eating fatty fish is one way to increase your omega-3 intake. It’s recommended to consume at least two, six-ounce pieces of fatty fish every week to meet expert recommendations.
BiOmega is a great solution if you can’t or don’t want to eat that much fish—because of food preferences or concerns over toxins associated with certain types of fish. Mercury or polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs—organic chlorine compounds) are usually the biggest concerns. Supplementing with quality fish oil is a safe and effective way to increase your omega-3 levels and help maintain a proper balance. And you can feel good about supporting your health without the fear of contamination that can come from eating certain types of whole fish.*
There’s Nothing Fishy About the Quality of USANA BiOmega Fish Oil
BiOmega is a whole-body oil (not a liver oil) made from anchovies and sardines—small fish with short lifespans. These fish are naturally much lower in contaminants than larger fish species, like swordfish and king mackerel. They also come from regulated sources to ensure quality. In fact, the raw material (pre-refining) oils used in BiOmega are already lower in PCBs than established guidelines for finished products.
The oil is concentrated and refined using fractional distillation. In other words, the chemical compounds are separated at different boiling points. This molecular distillation process removes impurities and any trans-fatty acids, leaving only the key beneficial components behind. The finished oil is tested once again for heavy metals and other contaminants to ensure it meets tough purity standards.
The fish oil comes from byproducts of fishmeal and canning industries. No fish are caught exclusively for the production of the oil. And any waste products are turned into biofuel to help power the production facility in Nova Scotia.
Good Health Starts with Good Cellular Function
BiOmega works to protect your good health at the most basic level—your cells. Let’s start by looking at how omega-3 fatty acids play a key role in cellular structure.
All of the cells in your body are enclosed in a plasma membrane. The fatty acids from your diet are incorporated into your cellular membranes to form a phospholipid bilayer (phospholipids are fatty acids combined with a phosphate). The membrane acts as a selective barrier—keeping things out or letting them in. It’s a gatekeeper that regulates the water, oxygen, nutrients, and other compounds that can cross the lipid barrier. Proteins in your cellular membrane are also how your cells send and receive communication signals.*
Because your cellular membranes are made up of the fatty acids from your diet, their rigidity or fluidity are directly impacted by what you eat. Rigid cell membranes don’t do you any favors. Stiff cells make it harder for the things your cells need to thrive to get in or out.
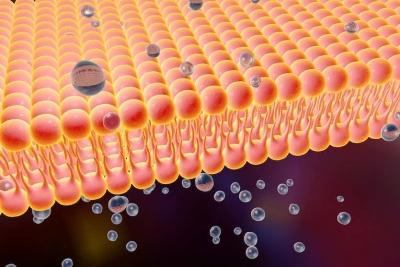
Ensuring the fluidity of cell membranes requires maintaining the right balance of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. If you consume too many saturated fatty acids, which are more rigid, your cell membranes might be rigid, too. Omega-3s, especially DHA, are one of the key structural fats you can consume to help maintain the fluid, healthy function of your cell membranes.*
Beyond being part of the structure of your cells, omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids serve many functions in your body. They are needed to produce a family of compounds called eicosanoids (prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes). These compounds are hormone-like substances that control many naturally occurring processes in your body, including vascular contraction and relaxation as well as blood clotting.*
With eicosanoids, it’s possible to have too much of a good thing. If there’s excessive arachidonic acid—an omega-6 fatty acid—in your cellular membranes, the result can be an overproduction of eicosanoids. This, in turn, may eventually lead to tissue damage.
Maintaining a good ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 in your cells acts like a check-and-balance system. Having enough omega-3s helps control the amount and types of eicosanoids made to help keep your cellular activities normal and balanced. Some of these activities can include promoting healthy immune function and responses to stress.*

Other than influencing eicosanoids, omega-3s also support healthy cell signaling and normal gene expression.*
Similarly, the vitamin D in BiOmega partners with the omega-3s to support cell health. There are vitamin D receptors on virtually every cell in your body. This fact illustrates how important vitamin D is for the health and function of your entire body. But the overwhelming majority of people are deficient in this vital nutrient, too. BiOmega gives you an added boost to help you get enough every day.*
The nutrients in BiOmega are vital for supporting many aspects of your health. That’s because they have a broad impact on your physiological function at the most fundamental level. *
BiOmega Works at the Heart of Cardiovascular Health
Fatty fish has long been a staple of the heart-healthy Mediterranean and DASH diets. And for good reason. Omega-3s and fish oil are swimming in benefits for cardiovascular health. Those benefits have been verified in a number of large-scale epidemiological studies and randomized, controlled studies.
How much do you need to get the cardiovascular benefits? The American Heart Association recommends two servings of fatty fish per week, supplementing with fish oil if needed. The Global Organization for EPA and DHA Omega-3s (GOED) suggests omega-3 intakes of 500 to 1000 mg per day. And some studies have shown advantages at even higher intakes.*
The concentrated levels of EPA and DHA in BiOmega were designed with your heart health in mind. How does BiOmega love your heart? Let’s count the ways:*
- Supportive, but not conclusive research, shows that consumption of EPA and DHA may reduce the risk of coronary heart disease. One serving of BiOmega provides 1050mg of EPA and DHA omega-3 fatty acids. [See nutrition information for total fat, saturated fat, and cholesterol content].*
- EPA and DHA help maintain healthy high-density lipoprotein (HDL—the good cholesterol) and triglyceride (a type of fat) levels in plasma, which are important for supporting healthy arterial function and blood flow.*
- Higher levels of omega-3s in plasma have been associated with maintained, normal blood pressure levels.*
- Consumption of omega-3 fatty acids in the diet is linked to endothelial health, which is important for healthy circulation.*
- Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids has been associated with arterial flexibility, a factor in good cardiovascular health.*
- Consuming one gram of marine omega-3 fatty acids per day has been associated with maintaining a healthy resting heart rate.*
BiOmega is Food for Your Brain
Your brain is your body’s master organ. It controls everything from breathing and balance to memory and mood. Good nutrition plays a significant role in maintaining overall brain health. You can feed your brain the beneficial fats it’s hungry for with BiOmega.*
Omega-3 fatty acids are a major component of your brain cells’ membranes. This makes omega-3s integral to your brain and central nervous system’s development, structure, and function. Healthy, fluid cell membranes help make sure chemical messages are sent and received by your neurons. This process is vital for cell communication, and it impacts learning, memory, and other complex cognitive processes.*
DHA is the major omega-3 fatty acid found in the brain. So, maintaining adequate levels helps support many brain functions, including normal enzyme and electrical activity as well as neurotransmission. This becomes especially important in your senior years. Lower levels of DHA have been associated with reduced brain volumes in older adults.*
A Look at How BiOmega Supports Eye Health
Your brain isn’t the only place with a lot of DHA. It also supports your eye health by naturally concentrating in the retina. This light-sensitive part of your eyeball sends optic signals to the brain, where a visual image is formed. DHA protects eye cells, supports the fluidity of photoreceptor membranes, and helps preserve retinal integrity. *
Further, DHA can help keep that healthy glisten in your eyes. It lubricates your eye to preserve normal vision and eye comfort. It does this by supporting the activity of a gland in your eyes that produces the oily part of tears.*
Some of the omega-3 benefits already discussed for heart health may play a role in your eyes, too. Your eyes contain tiny blood vessels. And by supporting vascular health, omega-3s in BiOmega can also help protect healthy eye function.*
Omega-3s Support Healthy Pregnancy and Healthy Babies
BiOmega should be a key part of your daily diet if you are expecting, may become pregnant, or are breastfeeding. A quality prenatal vitamin, like Prenatal CellSentials, gives you the important vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants you need. BiOmega delivers the omega-3s that will help support a healthy pregnancy, a stable mood after delivery, and normal fetal growth and development.*
Why supplement? It is almost impossible to get the increased levels of DHA and EPA needed during pregnancy from diet alone. And many mothers wisely avoid seafood during pregnancy and breastfeeding because of concerns about contaminants. That’s a significant impact to omega-3 intakes. A supplement can help you get the adequate amounts of DHA and EPA you need without any pollutant concerns.*
BiOmega fish oil can help give your baby a smart start in life. DHA is one of the dominant fats in the nerve cells of fetal and infant brains. Observational studies have found that omega-3 fatty acid consumption during pregnancy is associated with many different aspects of cognitive development in the child. All of the following have been related to omega-3 intake levels during pregnancy:*
- Visual recognition/memory
- Verbal intelligence
- Behavior
- IQ
- Fine motor skills
- Social skills
- Communication skills
Your baby’s need for healthy fats doesn’t end at birth. Continued omega-3 supplementation during breastfeeding has been shown to further support cognitive development.*

Omega-3s also help support healthy development of the eyes and visual system. Neural phospholipid membranes selectively concentrate DHA in photoreceptors and some cell-signaling sites. The retina selectively incorporates EPA to support eye fluidity. Some research has shown that if a mother has insufficient DHA during pregnancy, her infant may have below average visual acuity at 60 days of age.*
Prenatal consumption of omega-3 fatty acids has also shown benefits for healthy childhood lung function.*
In addition to the developmental benefits listed above, EPA and DHA are also important components for overall health in young children, adolescents, and young adults. Infant formulas with added DHA can further support development of your baby’s brain. And children over age four can start omega-3 supplementation with USANA BiOmega Jr. through adolescence.*
Beauty Goes Beyond Skin Deep with BiOmega
Nutritional skincare plays a role in the appearance of your skin. You can help a healthy-looking complexion by adding BiOmega to your daily beauty routine.
Deficiency in essential fatty acids can cause skin to become dry and lose its luster. While omega-3s are not the major fatty acids in the skin, dietary supplements can ensure you have the sufficient levels needed to help maintain skin’s barrier function. Of course, you’ll still want to use smart sun protection, too.*
Put BiOmega in Your Gym Bag for Fit Body Benefits
You exercise to keep your body fit. BiOmega can help you do even more to achieve your fitness goals. Research has shown combining fish oil intake with regular exercise is more supportive than exercise alone. This is especially true for helping to maintain a healthy weight and body fat, as well as supporting metabolic health.*
BiOmega can also help your body recover from the impact of exercise, so you can keep going strong. Fish oil supports joint function and helps maintain the health of the articular cartilage that covers the end of your bones, where they come together. After a workout, the nutrients in BiOmega may help reduce muscle soreness. Plus, they help support strong, healthy bones. Omega-3 supplements can also help support the body’s normal, healthy inflammatory response from exercise and everyday activities.*
Usage
Take two (2) capsules daily, preferably with food.
Ideal For
- All healthy adults over 18
- Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding
Frequently Asked Questions About USANA BiOmega
Why does fish oil dissolve Styrofoam?
What is the difference between BiOmega and BiOmega Jr.™?
USANA’s BiOmega supplement is a fish oil supplement that contains a balanced, concentrated source of beneficial omega-3 fatty acids including EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) in a convenient capsule form.
USANA’s BiOmega Jr. is a fish oil supplement that delivers appropriate amounts of the omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and vitamin D, in a delectable, sugar-free, flavored gel format that is friendly for kids or adults who have a hard time swallowing capsules.
How much EPA and DHA are in BiOmega?
Each serving (2 capsules) of BiOmega has 1200 mg total of omega-3 fatty acids. Of which 580 mg are eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and 470 mg are docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Can BiOmega™ be used during pregnancy and lactation?
Research has clearly shown that essential fatty acids are important for developing babies, and many women don’t get enough from diet alone. During pregnancy, omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA, support brain, eye, and nerve development, especially during the last trimester.*
How is BiOmega purified?
BiOmega™ is purified using high vacuum molecular distillation. (We actually distil the product twice to ensure a maximum level of purity.)
Molecular distillation removes impurities (heavy metals, dioxides, etc.), saturated fats, and other undesirable organic compounds, leaving only the key beneficial components of the fish oil. Molecular distillation is gentle with exceptionally low heat residence time and is performed in a vacuum to further reduce heat requirement. Additionally, the BiOmega is a whole-body oil (not a liver oil) made from wild caught anchovies and sardines – small fish with short lifespans which are naturally much lower in contaminants than larger fish (such as salmon, tuna, etc.)
Does BiOmega contain trans fat?
All of USANA’s products, including BiOmega, are completely free of trans-fatty acids.
Does BiOmega contain vitamin A?
No, BiOmega does not contain vitamin A. Unless added by the manufacturer, only fish oil supplements specifically made from fish liver (such as cod liver oil) will contain vitamin A.
Can I remove the liquid from the BiOmega capsules?
A primary concern with opening BiOmega capsules is the difficulty involved in emptying the capsule completely, which may reduce the amount of active ingredients received. (Also, it can be difficult to mask the taste of extracted fish oil.)
Assuming taste isn’t a concern and the capsule can be emptied completely, there shouldn’t be a problem with consuming BiOmega this way. Just be sure to use the liquid immediately, as it was not designed to be exposed to air.
What fish species are used to make BiOmega™?
BiOmega™ is a whole-body oil (not a liver oil) made from anchovies and sardines – small fish with short life spans which are naturally much lower in contaminants than larger fish (such as salmon, tuna, etc.). In fact, the raw material (pre-refining) oils used in BiOmega are already lower in PCBs than established guidelines for finished products. It is then purified using a process called high vacuum molecular distillation (twice) and the finished product is tested again for heavy metals and other contaminants.
Why doesn’t BiOmega contain omega-6 or omega-9 fatty acids?
Fish oil typically contains minimal amounts of omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids. If a company were to add dietary significant amounts of these nutrients to a fish oil supplement, the size and/or number of capsules would have to be increased.
In addition, omega-6 fatty acids tend to be more prevalent in the diet than omega-3’s, and while omega-9 fatty acids are beneficial and healthy they are not considered “essential” (since the human body is capable of synthesizing them).
How do I eliminate the fishy aftertaste associated with fish oil supplements?
Lemon oil is added to BiOmega to help reduce the potential for fishy aftertaste.
If you still find the taste bothersome, try taking BiOmega with a meal.
What is the caloric content of BiOmega?
10 calories per capsule, 20 calories per daily dose
Does BiOmega™ contain gluten?
USANA tablets and capsules do not contain wheat, oats, rye, barley, or gluten.
For complete allergen information:
Can I take BiOmega if I am allergic to fish?
For individuals with a specific allergy to fatty fish (e.g. salmon, mackerel, herring, sardines, anchovies), BiOmega would not generally be recommended except on the advice of a physician.
For individuals with shellfish-specific allergies (e.g. shrimp, crab, lobster), BiOmega should not be a problem as it does not contain any shellfish ingredients.
References
Schools Physical Activity and Nutrition Survey (SPANS)
Surette M. 2008. The science behind dietary omega-3 fatty acids. CMAJ 178(2): 177-180.
Haag M. 2003. Essential fatty acids and the brain. Can J Psychiatry 48: 195-203.
Querques G, Forte Raimondo, Souied E. 2011. Retina and omega-3. J Nutr Metab [Internet] [accessed 11 April 2018] Available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3206354/
Dyall S. 2015. Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and the brain: a review of the independent shared effects of EPA, DPA, and DHA. Front Aging Neurosci [Internet] [accessed 5 April 2018] Available at https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2015.00052/full
You May Also Enjoy
Pregnancy Nutrition- Creating a Foundation for a Healthy Pregnancy and Baby
Pregnancy nutrition is key to having a healthy baby. Learn what it takes to create a healthy eating plan during the different stages of pregnancy.
Understanding the Facts About Dietary Fat
An overview of the chemical nature of dietary fats and their role in nutrition. Discover the difference between fat types and their place in your diet.
5 Delicious Heart Healthy Foods You’ll Love
Learn about five heart healthy foods and why they’re so good for the heart. Get tips on crafting a heart-healthy diet.
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food & Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.