The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has warned consumers to apply a healthy dose of caution before buying products advertised as having “miracle” ingredients, new and unproven delivery methods, or “guaranteed” results. Many of these “quick cures” are unproven, fraudulently marketed, useless, and in some cases dangerous.
Coral Calcium is promoted mostly on late night infomercials. The marketing practices of coral calcium exploit and exaggerate the known importance and function of calcium and attempt to tie those benefits to their “miraculous” product and its “miraculous” cures. The fact of the matter is that there simply isn’t any good or thorough scientific research on coral calcium – and certainly not enough to support claims of “miraculous results.”
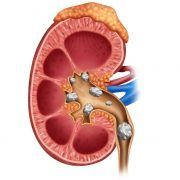
Coral reefs cover less than 1% of the planet’s surface, yet they are home to more than 25% of all marine life (over 4,000 different species of fish, 700 species of coral, and many other plants and animals). Coral reefs are among the world’s most fragile and endangered ecosystems, and strict laws are enforced to preserve them. Since it is illegal to mine live coral reefs, coral calcium must come from a different source. Some marketers of coral calcium attempt to circumvent this by stating that their ingredients are mined from old seabeds buried in the so-called “pristine” desert; or, mined from “fossilized coral sands that accumulated on the sea floor;” or, harvested from “only coral that washes up on the shore.”
The calcium content of coral calcium ranges from 24% to 38% and is composed primarily of calcium carbonate. This is often called “aragonite” or “calcite” to confuse and mislead the consumer into thinking it is something different than the standard forms of calcium already available to consumers.
The bottom line: coral calcium is simply a source of calcium carbonate.
Coral calcium is also touted as having a superior absorption rate. In reality, as long as it is tableted correctly and taken with a meal, calcium has a pretty standard absorption rate no matter what form it comes in. The RDAs for calcium are based on average absorption rates, so the recommended intakes already take into account the absorption rate in average persons.
Robert Heaney, M.D., a leading expert on calcium, has stated, “the advertising claims I’ve seen for coral calcium are outlandish. In the first place, all forms of calcium are poorly absorbed – and for good reason, to prevent dangerous ‘calcium intoxication.’ The idea that any calcium is 100 percent absorbed by the body is ridiculous and if true, would be potentially hazardous.”
In summary, here is what consumers need to know: the human body handles coral calcium just as it would any other calcium supplement. More importantly, there is usually more to a calcium supplement than just the source of calcium. Does the product contain adequate amounts of the other necessary nutrients for optimal bone health (vitamin D, silicon, boron, magnesium, vitamin K) or is it just a calcium product? Does it listelemental weights or complex weights? What is the delivery system?