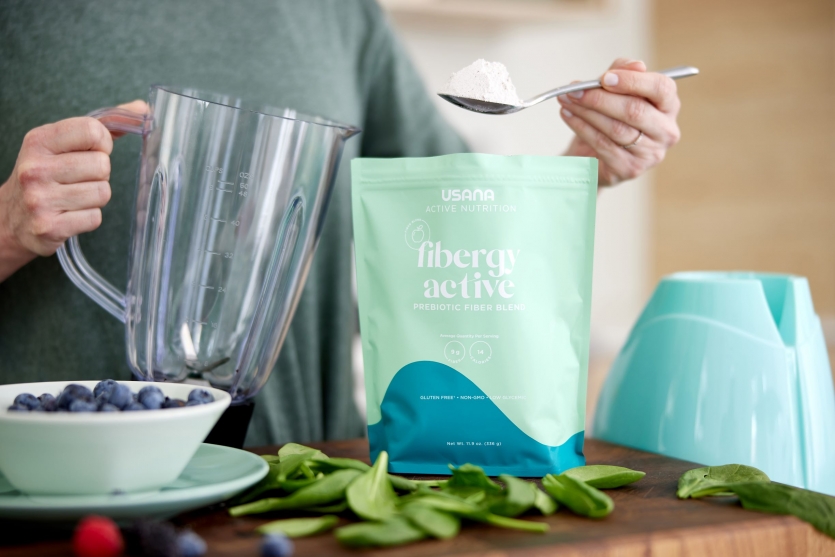
Gut Health and Digestive Support with Fibergy Active

Digestive health can be taken for granted. Healthy digestion is something you don’t notice if everything is operating smoothly. When your gut health isn’t intact, you might find an occasional upset stomach or irregularity draw all your focus. Fiber helps digestion stay smooth. And Fibergy Active is the fiber-focused solution in the USANA Active Nutrition product line that’s backed by science and thorough research to put optimal gut health within reach.
With Fibergy Active, you can show support for your gut health before irregularity and discomfort becomes a cross to bear. This fiber product is easy to put the health of your digestive system first. That’s because it’s no secret that fiber is important.
Fiber keeps the food you eat moving through your digestive system. It keeps the bacteria that live in your digestive tract happy and healthy. And the complex carbohydrate also keeps you feeling fuller longer, while supporting cardiovascular health. You can activate your gut to run smoothly, and support other important aspects of your overall health, with help from fiber.
It’s easy to add Fibergy Active to whatever drink you use to power your day. Green drinks, smoothies, meal-replacement shakes, even yogurt all mesh well with this versatile fiber supplement. So you have plenty of options to include more fiber in your diet.
Still wondering what fiber can do for you? Check out all the perks a digestive health product like Fibergy Active has to offer your overall health. And see how dietary fiber can help your gut and your body feel their best.
Fiber Keeps Your Gut Feeling Great
Meeting your daily fiber needs just became easier with Fibergy Active—a convenient, naturally low-glycemic way to up the ante on the complex carbs in your diet. And Fibergy Active is a blend of dietary fibers that are vegan-friendly and naturally sourced. So, you’ll get the full range of benefits that a variety of soluble and insoluble fibers have to offer.
As an active adult, you have a lot on your plate. You don’t need a sluggish digestive system slowing you down. Active Nutrition’s fiber support product Fibergy Active boasts a hefty nine grams of fiber that support your digestive system in key ways:
- Maintains good digestive health by aiding regularity
- Feeds and maintains your gut microbiome
- Supports good cardiovascular and metabolic health
- Actively supports weight management by helping you feel satisfied after meals
Digestive Health—How Much Fiber Do I Need?
If you want to take your health and fitness to the next level, look for ways to mix more fiber into your diet. Nine out of 10 people need to consume more fiber. Aim to be the one in ten people that meets their quota of this complex carbohydrate each day.
The average adult only eats about 16 grams of dietary fiber a day. But the recommended intake for total fiber are much higher, between 25 and 30 grams daily. It’s hard for your digestive system to operate at full strength with only half the fiber it needs every day.
But you can fortify your gut health with the help of fiber. A digestive support product like Fibergy Active knocks out a sizable chunk of your daily recommended fiber intake—about a third of the dietary fiber your gut depends on.
If you want to maintain regularity and support comfortable, dependable digestion, take an active role in your digestive health. Optimize it with the help of USANA Fibergy Active.
Stock Up on Soluble and Insoluble Fiber for Digestive Health
Fiber is the key that unlocks the door to healthy digestion. You can optimize your digestive health with a fiber product like Fibergy Active that works hard for your gut.
Dietary fiber comes in two varieties: soluble and insoluble. The soluble fibers mix well with water and take on a gel-like consistency that smoothly moves through your gut. Insoluble fibers add weight and bulk to the food you digest, coaxing it through your digestive tract so you can digest comfortably.
Explore the fiber components of Fibergy Active and learn how each supports and maintains your digestive health.
- Fructooligosaccharides (FOS) are the first ingredient in USANA Fibergy Active. They’re a mouthful to pronounce, but these short-chain fructose (sugar) molecules are small bits of soluble fiber that optimize the movement of food through your digestive tract. FOS occur naturally in many plants, and are a source of natural sweetness.
- Sugarcane fiber is another insoluble addition to Fibergy Active. It‘s a tried-and-tested component of many fiber products. That’s because sugarcane fiber supports regularity, which allows you to digest comfortably.
- Apple, blueberry, and raspberry powders are also included in the Fibergy Active formula. These fruit powders are full of phytochemicals and antioxidants that synergize with fiber to optimize your digestion.
Give your gut the fiber it needs to maintain healthy digestion. Regularity and comfort are a great way to measure the health of your digestive system. You need roughage to keep food moving through your gut. So adding a digestive support product like Fibergy Active can help support healthy digestion to keep your days running smoothly.
Fibergy Active Taps the Prebiotic Power of Organic Agave Inulin to Feed Your Microbiome
Healthy digestion begins with a well-nourished microbiome. If you’ve ever felt out-of-touch with the microbes living in your gut, fiber is your solution. The complex carbohydrate feeds the helpful bacteria that live in your intestines. These bacteria are necessary for digestion because they break down compounds that your body can’t on its own.
Fibergy Active makes it easy for you to feed your microbiome the prebiotic fiber it needs to thrive. Along with the fruit powders mentioned above, the formula has organic agave inulin to support the microflora that reside in your gut.
Agave inulin promotes the growth of bacterial strains like bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. These microbes support the digestive tract’s ability to break down foods and absorb nutrients. This helps your body maintain healthy levels of nutrients to help you conquer your daily grind.
Inulin feeds the beneficial bacteria in your gut through a process called fermentation. Here’s a quick lesson on how fermentation works:
- Fermentation is one biological method of breaking down carbohydrates into smaller constituent compounds, usually in environments where there is little to no oxygen. The products of fermentation can vary, but sugar and carbon dioxide are often produced.
- Bacteria are just one organism that utilizes fermentation. This chemical process makes bread dough rise, pickles sauerkraut, and brews alcoholic beverages like beer and wine. Your muscles perform lactic acid fermentation to create additional ATP when you exercise. On a much smaller scale, fermentation happens in your gut, too.
- Fermentation is the process bacteria in your gut use to extract energy from fiber, like those found in Fibergy Active, which are sources of energy for these gut bacteria.
- During fermentation your gut bacteria secrete digestive enzymes that break down complex carbohydrates like fiber into short-chain fatty acids, which support the growth of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli in the intestines.
- Prebiotic fibers also help the bacteria in your gut synthesize vitamins—specifically vitamin K and B vitamins.
The inulin in your diet—like the agave inulin in Fibergy Active—can also maintain the biodiversity of your gut microflora. You want to keep your microbiome diverse and well fed, because these beneficial bacteria help you digest the variety of food you eat.
You can access the full microbiome benefits of dietary fiber with the help of Fibergy Active. Bifidobacteria and lactobacilli need the support of inulin and other fibers to work optimally in your gut. Provide your digestive system with the fiber it needs by making Fibergy Active a part of your healthy diet.
Your Cardiovascular System and Blood-Sugar Benefit, Too
Fulfilling your daily roughage requirements can do more than keep you regular. Fiber may help maintain healthy blood sugar levels. By helping your body digest food over a longer period of time, Fibergy Active helps maintain healthy blood glucose levels, as long as they’re already in the normal range.
Your cardiovascular system will also thank you for prioritizing fiber in your diet. Low-density lipoproteins (or LDL cholesterol) take a toll on heart health. They’re “sticky” molecules that can build up in blood vessels.
But fiber is “sticky,” too. Complex carbs bind easily to LDLs, helping to support the liver process and eliminate them from the body. And all it takes to access this healthy cholesterol support is five to 10 grams of fiber each day. A single serving of Fibergy Active puts you right in the sweet spot with the nine grams of fiber.
You’re supporting the health of more than just your digestive system when you add a fiber supplement to your diet. So optimize your overall wellness by ensuring you consume the fiber your body needs each day with the help of Fibergy Active.
A Fiber Support Product Can Help Maintain a Healthy Weight
If you weren’t already convinced of the many benefits of dietary fiber, add healthy weight support to the list. Fiber products support overall health even further by helping you maintain a healthy weight.
Incorporating a fiber aid like Fibergy Active can support your weight-management goals. That’s because complex carbohydrates can curb cravings that might interfere with your dietary plan. And the bulking agents in Fibergy Active help you digest your food more slowly. This means you feel full for longer, and are less tempted to munch on unhealthy snacks.
Weighing in at only 15 calories per serving, you can be sure this fiber product won’t overturn your diet. Fibergy Active is truly a low-calorie, low-maintenance way to fill your daily fiber quota. So you can skip the extra snacks and maintain a healthy weight with the full-stomach feelings of Fibergy Active.
It’s Easy to Find a Room in Your Diet for Fibergy Active
Adding fiber to your diet is a simple way to take your nutrition to the next level. And a scoop of Fibergy Active—formulated with a neutral taste for ultimate versatility—in your protein shake or green drink is all it takes to support your fiber intake.
Sure you can maintain the recommended amount of roughage in your diet by adding this high-quality, low-glycemic fiber supplement to your daily routine. But meeting the minimum is just the beginning, though.
You may turn to Fibergy Active to maintain comfortable, effective digestion for regular days. But you’ll also be capitalizing on fiber’s weight-management power, as well as its support for cardiovascular health. And optimizing gut health, helping maintain healthy blood sugar levels already in the normal range, and supporting a healthy heart in one drink a day.
Make every day a day of digestive health with the fiber found in USANA Fibergy Active.
Key Ingredients
- Fructooligosaccharides
- Organic Agave Inulin
- Sugarcane Fiber
- Apple, raspberry, and blueberry powders
Usage
Add one (1) tablespoon to your USANA Meal Replacement shake.
Ideal For
Individuals looking for a reliable source of dietary fiber to add to their diet.
References
https://www.webmd.com/diet/compare-dietary-fibers
https://botanical.pbrc.edu/pdf/Hsia%20Botanical%20Symposium%202014.pdf
https://www.ucsfhealth.org/education/increasing-fiber-intake
https://www.healthline.com/health/bifidobacterium-bifidum
http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/digestion/largegut/ferment.html
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food & Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.