MagneCal D™
Build Your Bone Health and Beyond with USANA® MagneCal D™
USANA® MagneCal D™
Build a strong foundation for your active life with a carefully balanced bone-building supplement.*
Make no bones about it, calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D are all vital to your everyday health. The good news is that dietary surveys show most people are generally consuming more calcium now than in recent decades. The bad news? Overall calcium consumption is still falling a bit short of optimal dietary amounts. And the majority of people fall significantly far below adequate intakes of magnesium or vitamin D.*
By consuming more calcium than magnesium, you may have an imbalance that, according to researchers, could negatively impact your long-term health. The Center for Magnesium Education and Research recommends something close to a 2:1 ratio of total calcium to magnesium per day—from food and supplements.
Vitamin D is another nutrient that continues to show benefits up to as much as 125 mcg per day. And it has repeatedly been shown that calcium is most beneficial when taken with vitamin D and magnesium.*
Long story, short: you probably need more magnesium and vitamin D than you’re already getting. But not necessarily a lot more calcium.*
Fortunately, supplementing these key nutrients is easy. And, it’s one of the best ways to reach more ideal levels. However, most calcium supplements provide much more calcium than magnesium—making the imbalance worse. USANA® MagneCal D™ is different. It offers a 1:1 ratio of magnesium and calcium.*
This equal ratio means you get more magnesium—but not a lot of extra calcium—to help you get closer to the overall 2:1 ratio. Plus, you get advanced levels of vitamin D. Together, this formula delivers a better balance that matches today’s dietary needs.
MagneCal D can help you maintain many aspects of good health.* Here are just a few:
- Strong, mineral-rich bones and teeth*
- Healthy muscle and nerve function*
- Energy metabolism*
- Cardiovascular health*
The kosher formula is an excellent complement to the USANA® CellSentials™. Together, they will help give you optimal amounts of nutrients with excellent absorption and maximum effectiveness.*
It’s Elemental—USANA MagneCal D Builds Your Bone Stores
Calcium and magnesium are important for many different physiological processes that keep you healthy. Calcium is the most abundant mineral in your body. And while there isn’t as much magnesium, it’s certainly no less important. Magnesium is vital for your health. It’s required to activate more than 300 enzyme reactions. Some of these reactions include helping your body make things, like protein, DNA, RNA, and glutathione.*
The majority of calcium and magnesium in your body is stored in your skeleton. In fact, 99 percent of calcium is found in your teeth and bones. About 60 percent of magnesium is stored there. The remaining calcium and magnesium reside in your tissues and bloodstream.*
The levels of calcium and magnesium in your bloodstream are tightly regulated by the body. Calcium and magnesium are pulled from your bones when needed to maintain steady levels. This process is called “resorption,” and it means your body is re-absorbing those minerals. It’s also a key part of the normal bone remodeling process, in which your body breaks down and reforms new bone.*
This remodeling process requires sufficient amounts of magnesium, calcium, and vitamin D to be available from the diet to help reform the bones properly. These nutrients all work together—along with other elements like phosphorus, silicon, and boron—to ensure proper calcium utilization and absorption.
Magnesium is also a cofactor that helps the body use vitamin D. So, if you don’t have enough calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D available from your diet, your blood- and bone-mineral levels may be negatively affected.*
If you don’t eat much dairy, leafy green vegetables, nuts, or fortified foods you may not get enough calcium, magnesium, or vitamin D. Drinking coffee, soda, or alcohol may further deplete your magnesium levels. And if you regularly wear sunscreen or stay out of the sun, you very likely need more vitamin D.*
MagneCal D helps boost your dietary intakes to help build up your bone stores of calcium and magnesium. MagneCal D contains blends of these essential minerals in citrate and carbonate forms. Together, these blends absorb well and may be gentler on your digestive system.
Added vitamin D helps ensure your body can use the calcium most effectively. This is in addition to the essential vitamin’s many benefits for cellular function and whole body health. MagneCal D uses vitamin D3 from cholecalciferol—the same form of vitamin D that’s naturally made in the body. *
MagneCal D also contains silicon and boron. Silicon is found in active growth areas where it’s thought to promote bone growth and hasten mineralization. The mineral also gives stability to connective tissues. Boron may play a role in bone maintenance by reducing calcium excretion and increasing deposition of calcium in the bone.*
A Strong Body Starts with Your Bones
Your skeletal system is your greatest supporter—your source of inner strength. It literally bears the weight of your world. This interconnected system is made of more than 200 bones plus tendons, ligaments, and cartilage that joins them.*
Bones are the major part of your skeleton. They give your body structure and hold you up and protect your internal organs. Bones are a site of red blood cell production. And, as mentioned above, your bones store minerals needed to support many physiological processes.*
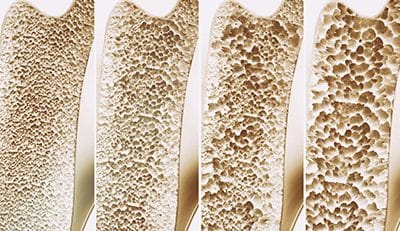
Your bones are made of hard, dense connective tissue on the outside and a spongy inner layer that is lighter and less dense on the inside that is always changing. The entire skeletal structure constantly remodels itself. New bone is always being built to replace old bone that’s being torn down. In 10 years, you’ll have a completely new skeleton.*
You reach peak bone mass by early adulthood. So, you want to do everything you can to build your bones through your late twenties. Then, do what you can to preserve what you have. Your bone mass will begin to gradually decrease after about the age of 25. And, as part of the normal aging process, women after menopause begin to lose bone mass more rapidly.*
Keeping your bones strong hinges on having enough calcium and magnesium available during the remodeling process. If your body consistently uses more of these nutrients than are replaced, it may lead to bone loss.*
If you lose too much bone mass or your body doesn’t make enough new bone, it can lead to frailty, osteopenia (weakened bones), or osteoporosis. The word for this medical condition means “porous bones.” It causes bones become brittle and fragile from loss of tissue. Bones can become so fragile that minor falls or stresses can cause a fracture. In extreme cases, even coughing or sneezing can break a bone. Likewise, without sufficient vitamin D, bones can become thin, brittle, or misshapen.*
Help your bones stand strong with MagneCal D. Adequate vitamin D and calcium, as part of a healthy diet, along with physical activity, may reduce the risk of osteoporosis in later life. Several population-based studies have found positive associations between magnesium intake and bone-mineral density in both men and women. Consistently higher intakes of the nutrients in MagneCal D have also shown benefits in preserving bone-mineral density for post-menopausal women.*
Along with good oral care, the nutrients in USANA’s MagneCal D can help support healthy teeth, too. Preserving bone density helps protect the health of your pearly whites. Calcium and adequate vitamin D levels have also been linked to maintaining healthy gums.*
Skeletal Support for Your Muscles and Nerves Helps Keep You Moving
A sturdy skeleton involves more than your bones. Your muscles work with your bones and joints to keep your body aligned and moving. The muscular system is made up of skeletal muscle tissue, blood vessels, tendons, and nerves.*
By promoting healthy bone mineralization, the ingredients in MagneCal D give you more complete neuromuscular support. It helps ensure your body has what it needs for proper muscle and nerve function.*
Nerves cells known as motor neurons play a role in muscle function. They do this by transmitting information from the brain, telling your muscles to contract or relax. Calcium and magnesium in your bloodstream are needed for those electrical signals and reactions. So, keeping the two elements in balance helps maintain proper muscle function.*
Vitamin D also helps maintain normal functioning of the nervous system. It helps maintain calcium balance, and has also been associated with the production and release of proteins needed for normal nerve cell signaling.*
The fat-soluble vitamin can also influence muscle strength, especially in people over 50. Studies have shown a higher level of vitamin D in the body is correlated with preserved muscle health. Keeping muscles strong is essential for maintaining physical performance—a key part of staying active and independent throughout life.*
Be Good to Your Heart with MagneCal D
Your heart is a muscle. This tissue is responsible for making your heart contract and relax to pump blood through your body. So, supporting healthy muscle function and electrical conduction can help keep your heart beating strong. (Muscle tissue is also found in other organs and parts of your body, including your digestive system.)*
That’s just one of the ways MagneCal D can help support your heart.*
Getting the proper balance of nutrients is the key to a supplement’s ability to help maintain heart health. You wouldn’t want to supplement with calcium alone. You need a blend of nutrients that helps ensure calcium is deposited in your bones.*
Magnesium and vitamin D, in addition to calcium, are the key to showing your heart some love with a supplement. Supplementing with vitamin D or magnesium has been shown to help maintain healthy, normal blood pressure (already in the normal range).*
Adequate amounts of magnesium and vitamin D have been linked to support for healthy blood flow in two important ways:
- Supporting normal endothelial function. Endothelial cells are responsible for telling your blood vessels to expand and contract. They also support healthy blood clotting, which also requires calcium ions to function properly.*
- Supporting arterial elasticity. The artery’s ability to expand and contract helps maintain normal blood flow. *
A heart-smart partner for MagneCal D is USANA Vitamin K2. It’s a critical nutrient for ensuring calcium from your diet is absorbed by your bones and not by your blood vessels. This action helps maintain healthy, flexible arteries to protect normal cardiovascular function.*
Of course, as part of your overall healthy lifestyle, consume plenty of fruits and veggies, low or non-fat dairy, and less fat to help protect your heart.*
Help Keep Your Energy and Blood Glucose Levels Steady
Your body gets the energy it needs to function from different sources. The magnesium in MagneCal D help support healthy metabolism to break down fats, carbohydrates, and sugars from food into useable energy sources.*
The simple sugar glucose breaks down into glycogen—a preferred energy source for your brain, red blood cells, and muscles. However, too much sugar in the blood can be unhealthy. That’s why it’s important to limit excess sugar and refined carbohydrates from your diet to help keep your blood glucose levels in a healthy range.*
MagneCal D can also help. Intakes of calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D have all been associated with maintaining normal blood sugar levels, provided they are already healthy. This is likely, at least in part, because of the role these nutrients play in supporting overall cell health. They also participate in the complex reactions that regulate how your body responds to sugar.*
Magnesium is also a critical part of the metabolism process that helps energize your cells. It provides important support to your mitochondria—your cellular power plants. And, magnesium is needed during production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)—the energy that powers cellular function. This cellular energy must be bound to a magnesium ion to become biologically active.*
Maintain a Balanced Mood with MagneCal D
The benefits of MagneCal D extend beyond a strong skeleton to other forms of inner strength. It can also support a balanced mood.
Your mood involves an interplay of many factors, including genetics and biochemistry, lifestyle habits, and dietary patterns. A healthy diet has been linked to positive mood. On the other hand, unhealthy food choices and deficiencies in foundational nutrients have been linked to poor mood.*
You can support brain health with a quality multivitamin like the CellSentials, which will help ensure you get a full range of essential nutrients. MagneCal D also helps you avoid deficiency of two nutrients shown to be helpful for maintaining a balanced mood—magnesium and vitamin D. Both support healthy functions in the brain:*
- Magnesium helps support healthy neuronal function. Neurons send and receive chemical and electrical signals via messengers called neurotransmitters. Maintaining normal function of this process is vital for healthy brain activity and mood.*
- Vitamin D receptors are extensive in brain tissue. The D3 form has been shown to be neuroprotective. Supplementation of at least 600 IU of the sunshine vitamin per day (also in combination with vitamin A) has suggested benefits in perceptions of well-being.*
Usage
Adults take two (2) tablets twice daily, preferably with food.
Ideal For
- All healthy adults over 18
- Certified Kosher (U.S. formula)
Frequently Asked Questions About USANA MagneCal D
How does coral calcium compare to the calcium used in MagneCal D?
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has warned consumers to apply a healthy dose of caution before buying products advertised as having “miracle” ingredients, new and unproven delivery methods, or “guaranteed” results. Many of these “quick cures” are unproven, fraudulently marketed, useless, and in some cases dangerous.
Coral Calcium is promoted mostly on late night infomercials. The marketing practices of coral calcium exploit and exaggerate the known importance and function of calcium and attempt to tie those benefits to their “miraculous” product and its “miraculous” cures. The fact of the matter is that there simply isn’t any good or thorough scientific research on coral calcium – and certainly not enough to support claims of “miraculous results.”
Coral reefs cover less than 1% of the planet’s surface, yet they are home to more than 25% of all marine life (over 4,000 different species of fish, 700 species of coral, and many other plants and animals). Coral reefs are among the world’s most fragile and endangered ecosystems, and strict laws are enforced to preserve them. Since it is illegal to mine live coral reefs, coral calcium must come from a different source. Some marketers of coral calcium attempt to circumvent this by stating that their ingredients are mined from old seabeds buried in the so-called “pristine” desert; or, mined from “fossilized coral sands that accumulated on the sea floor;” or, harvested from “only coral that washes up on the shore.”
The calcium content of coral calcium ranges from 24% to 38% and is composed primarily of calcium carbonate. This is often called “aragonite” or “calcite” to confuse and mislead the consumer into thinking it is something different than the standard forms of calcium already available to consumers.
The bottom line: coral calcium is simply a source of calcium carbonate.
Coral calcium is also touted as having a superior absorption rate. In reality, as long as it is tableted correctly and taken with a meal, calcium has a pretty standard absorption rate no matter what form it comes in. The RDAs for calcium are based on average absorption rates, so the recommended intakes already take into account the absorption rate in average persons.
Robert Heaney, M.D., a leading expert on calcium, has stated, “the advertising claims I’ve seen for coral calcium are outlandish. In the first place, all forms of calcium are poorly absorbed – and for good reason, to prevent dangerous ‘calcium intoxication.’ The idea that any calcium is 100 percent absorbed by the body is ridiculous and if true, would be potentially hazardous.”
In summary, here is what consumers need to know: the human body handles coral calcium just as it would any other calcium supplement. More importantly, there is usually more to a calcium supplement than just the source of calcium. Does the product contain adequate amounts of the other necessary nutrients for optimal bone health (vitamin D, silicon, boron, magnesium, vitamin K) or is it just a calcium product? Does it listelemental weights or complex weights? What is the delivery system?
Can taking MagneCal D upset my stomach?
Higher intake of supplemental magnesium can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort. If you experience any discomfort, try reducing your daily dosage and gradually increasing to your desired levels of daily intake.
Is it possible to take too much calcium?
Adverse effects of calcium in normal adults have been observed with chronic intakes above 2500 mg/day. The upper tolerable limit for adults 51 and older is 2000 mg/day.
References
Jugdaohsingh, R. Silicon and Bone Health. J Nutr Health Aging. 2007 Mar-Apr; 11(2): 99–110.
Nieves JW. Osteoporosis: the role of micronutrients. 2005. Am J Clin Nutr 81(5):1232S-9S.
Larsson SC, Wolk A. 2007. Magnesium intake and risk of… J Intern Med 262(2): 208-14.
Anastassios G, et al. 2006. Vitamin D and calcium intake in relation to… Diab Care 29(3): 650-656.
Anastassios G, Lau J, Hu F, Dawson-Hughes B. 2007. The Role of Vitamin D and Calcium in type 2 diabetes. A systematic Review and Meta-Analysis* J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(6) : 2017-2029.
Wrzosek M, et al. 2013. Vitamin D and the central nervous system. Pharmacol Rep 65(2): 271-8.
Wang, et al. 2008. Vitamin D deficiency and risk of cardiovascular… Circulation 117: 503-511.
Tarleton EK, et al. 2017. Role of magnesium supplementation in the treatment of depression: A randomized clinical trial. PLoS One 12(6) [Internet] [accessed 20 Mar 18] Available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28654669
Boyle NB, Lawton C, Dye L. 2017. The Effects of Magnesium Supplementation on Subjective Anxiety and Stress—A Systematic Review. Nutrients 9(5): 429. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5452159/
Soni M, et al. 2012. Vitamin D and cognitive function. Scand J Clin Lab Supl [Internet] [accessed 20 Mar 2018] Available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22536767
Other resources:
The Surgeon General’s Report on Bone Health and Osteoporosis: What It Means to You
You Might Also Enjoy
Bone Health: Understanding Bone Anatomy
Your bone anatomy makes your skeleton more than your body’s framework. Learn about your skeletal system and how you can support your bone health.
Your Guide to Essential Minerals
Your body needs minerals to operate properly. Learn about the essential minerals you need to achieve your best health.
The 8 Pillars of Holistic Health and Wellness
Learn the eight pillars that support your holistic health and wellness, and help you live your best life.
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food & Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.